Understanding Autism Prevalence
Autism prevalence refers to the proportion of individuals diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) within a given population at a specific point in time. It is a critical metric that helps stakeholders understand the scale and impact of ASD on communities and societies.
Definition of Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorder is a complex developmental condition that involves persistent challenges in social interaction, speech and nonverbal communication, and restricted/repetitive behaviors. The effects of autism and the severity of symptoms can vary widely among individuals. ASD is known as a 'spectrum' disorder because there is wide variation in the type and severity of symptoms people experience.
Importance of Prevalence Data
Prevalence data on autism is crucial for several reasons. It helps in:
- Identifying the Scope of ASD: Understanding how widespread autism is within a population informs healthcare providers, educators, and policymakers about the level of resources and support that need to be allocated.
- Informing Research and Funding: Accurate prevalence data drive research priorities and funding allocations, ensuring that efforts are directed where they are most needed.
- Supporting Diagnosis and Intervention: Knowing how many people are affected by ASD can lead to improved diagnostic services and early intervention strategies, which are key for better long-term outcomes.
- Shaping Public Health Strategies: Prevalence rates can influence the development of public health strategies and help in the implementation of targeted educational programs and support services.
For more detailed information on the prevalence of ASD, readers can explore autism spectrum disorder statistics, which provide a comprehensive overview of the condition's impact on various demographics, including the analysis of autism prevalence by gender. This data is crucial for assessing the needs of individuals with ASD and ensuring they receive the appropriate support and resources. Additionally, understanding autism prevalence worldwide gives a broader perspective on how autism affects populations globally and highlights the importance of international collaboration in autism research and services.
Global Autism Statistics
The investigation into global autism statistics is pivotal for understanding the broader impact of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) across different populations and regions.
Worldwide Prevalence Rates
Autism is a condition that knows no borders, affecting individuals globally. The worldwide prevalence rates of autism have been the subject of many studies, with numbers varying based on the diagnostic criteria and methods used. Current research indicates that roughly 1 in 160 children has an autism spectrum disorder.
| Region | Estimated Prevalence |
|---|---|
| North America | 1 in 68 |
| Europe | 1 in 100 |
| Asia | 1 in 160 |
| Africa | Data Varies Widely |
These figures underscore the significance of autism as a global health concern. For an in-depth look at the statistics, readers can explore the autism prevalence rates in various countries.
Regional Variances
Regional variances in autism prevalence are not just about differing rates; they reflect the influence of socioeconomic factors, awareness levels, and access to healthcare services. In many regions, underdiagnosis or lack of diagnostic facilities can lead to lower reported rates of autism. Conversely, areas with greater awareness and better diagnostic practices may report higher prevalence rates.
For instance, the United States and South Korea have some of the highest reported prevalence rates of ASD, which may be attributed to heightened awareness and comprehensive screening practices. Meanwhile, in many low- and middle-income countries, limited resources and less awareness can result in lower reported rates, though the actual prevalence may be similar.
| Region | Factors Influencing Reported Prevalence |
|---|---|
| North America | High awareness, advanced diagnostic services |
| Europe | Varying diagnostic criteria, social awareness |
| Asia | Cultural factors, economic disparities in healthcare |
| Africa | Limited resources, varying levels of awareness |
Understanding these variances is crucial for global health initiatives and resource allocation. To learn more about the nuances in regional autism statistics, readers can visit the article on autism prevalence worldwide.
These global and regional statistics set the stage for more localized data analysis, such as within the United States, where state-specific data helps to further tailor support and resources. Moreover, recognizing these variances allows for better-informed discussions on the topic of autism prevalence by gender, which is a key issue in understanding the gender divide in autism diagnosis.
Autism Prevalence in the US
The examination of autism prevalence in the US provides valuable insight into the scale and scope of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) within the nation. Understanding these statistics is essential for allocating resources, planning services, and raising awareness about the condition.
National Statistics
Nationally, ASD affects a significant number of individuals. According to the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the most recent data indicates that approximately 1 in 54 children has been identified with ASD. This statistic underscores the importance of understanding and addressing autism, as it illustrates the widespread impact of the disorder across the country.
| Age Group | Prevalence (per 1,000 children) |
|---|---|
| 8 years | 18.5 |
It's critical to note that these figures are continuously evolving as diagnostic criteria and awareness of ASD change over time. To stay informed about autism spectrum disorder statistics and autism diagnosis rates, one must keep abreast of the latest research and reports.
State-Specific Data
The prevalence of ASD varies across states due to factors such as diagnostic practices, availability of services, and population demographics. For instance, some states may have higher reported rates of autism due to better access to diagnostic services or more comprehensive reporting systems.
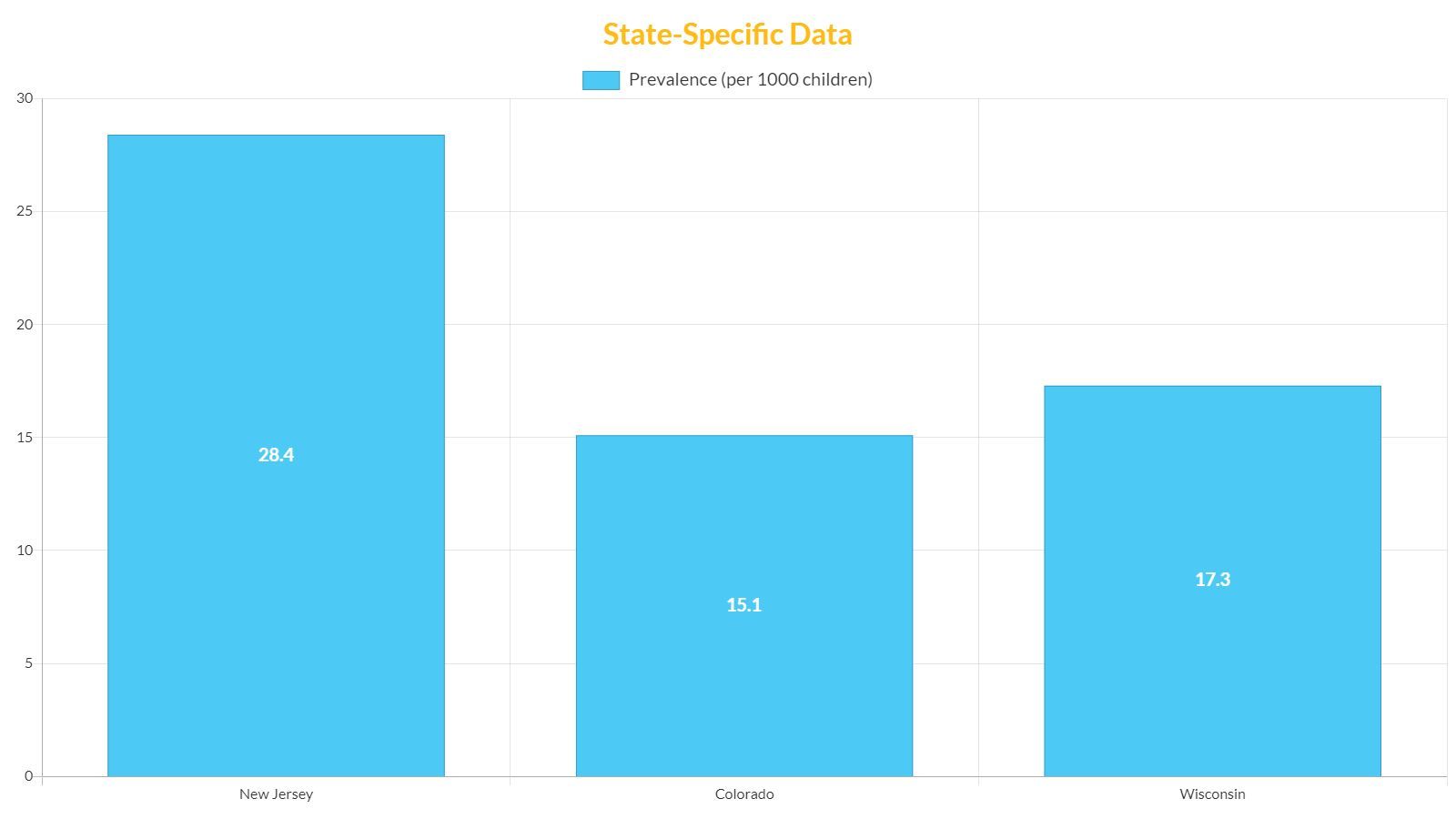
This state-specific data can be vital for local policymakers and advocacy groups who are working to ensure that individuals with ASD have access to the support and resources they need. For more detailed information about state-specific autism prevalence, readers may refer to our comprehensive guide on autism prevalence rates.
Understanding the prevalence rates on both a national and state level allows stakeholders to gauge the impact of autism within various communities. This data serves as a foundation for targeted interventions, resource allocation, and long-term planning for individuals with ASD and their families. Additionally, comparing US data with autism prevalence worldwide can offer a broader perspective on how autism is understood and addressed globally.
Gender Disparities in Autism
The exploration of gender disparities in autism spectrum disorders (ASD) is a critical area of study, as it holds implications for diagnosis, support, and understanding of this condition. The prevalence of autism has been observed to differ between genders, prompting further investigation into the underlying causes.
Prevalence by Gender
Historically, autism has been diagnosed more frequently in males than in females. The
autism
prevalence by gender shows a ratio that is commonly cited as 4:1, meaning that for every four males diagnosed with ASD, there is typically one female. However, these figures can vary, and recent studies suggest that the gender gap may be narrower than previously thought.
| Gender | Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Male | 1 in 42 |
| Female | 1 in 189 |
These figures reflect a significant disparity in autism diagnosis rates between genders and highlight the need for increased awareness and understanding of how autism manifests differently across the gender spectrum.
Factors Influencing Gender Differences
Several factors may contribute to the difference in autism prevalence by gender. One primary consideration is the potential for underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis in females, as they may exhibit less overt symptoms compared to their male counterparts. This can lead to females with ASD not receiving the diagnosis or support they need.
Other factors influencing these gender differences include:
- Biological and genetic factors: Research suggests that there may be genetic protective factors at play that make females less susceptible to developing ASD.
- Societal and cultural expectations:
There is a hypothesis that societal norms and expectations around gender behaviors may influence the recognition and diagnosis of autism.
- Presentation of symptoms: Females with ASD might present with symptoms that are less aligned with the traditional diagnostic criteria, which were initially based on male characteristics of the condition.
The understanding of how gender influences autism diagnosis is evolving, with ongoing research seeking to provide a more nuanced view of these disparities. For a comprehensive look at autism spectrum disorder statistics, including the latest findings on gender differences, readers can explore our dedicated section on the topic.
Recognizing the importance of gender in understanding autism prevalence is essential for tailoring interventions and support to meet the needs of all individuals on the autism spectrum. As research continues to shed light on these disparities, it is crucial for parents, professionals, and educators to stay informed and consider gender as a factor in both the diagnosis and support of individuals with ASD.
Autism Prevalence Trends
The prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) has been the subject of numerous studies over the years. Assessing these trends is crucial for understanding the changes in diagnosis rates and the potential factors contributing to these shifts.
Historical Perspective
Historically, the prevalence of autism has seen a significant increase. In the 1970s and 1980s, autism was believed to be a relatively rare condition, with estimated rates of about one in every 2,000 children. Over time, these numbers have grown substantially. Changes in diagnostic criteria, greater awareness of the condition, and improved detection methods have all been suggested as reasons for this increase.
Table: Historical Trends in Autism Prevalence
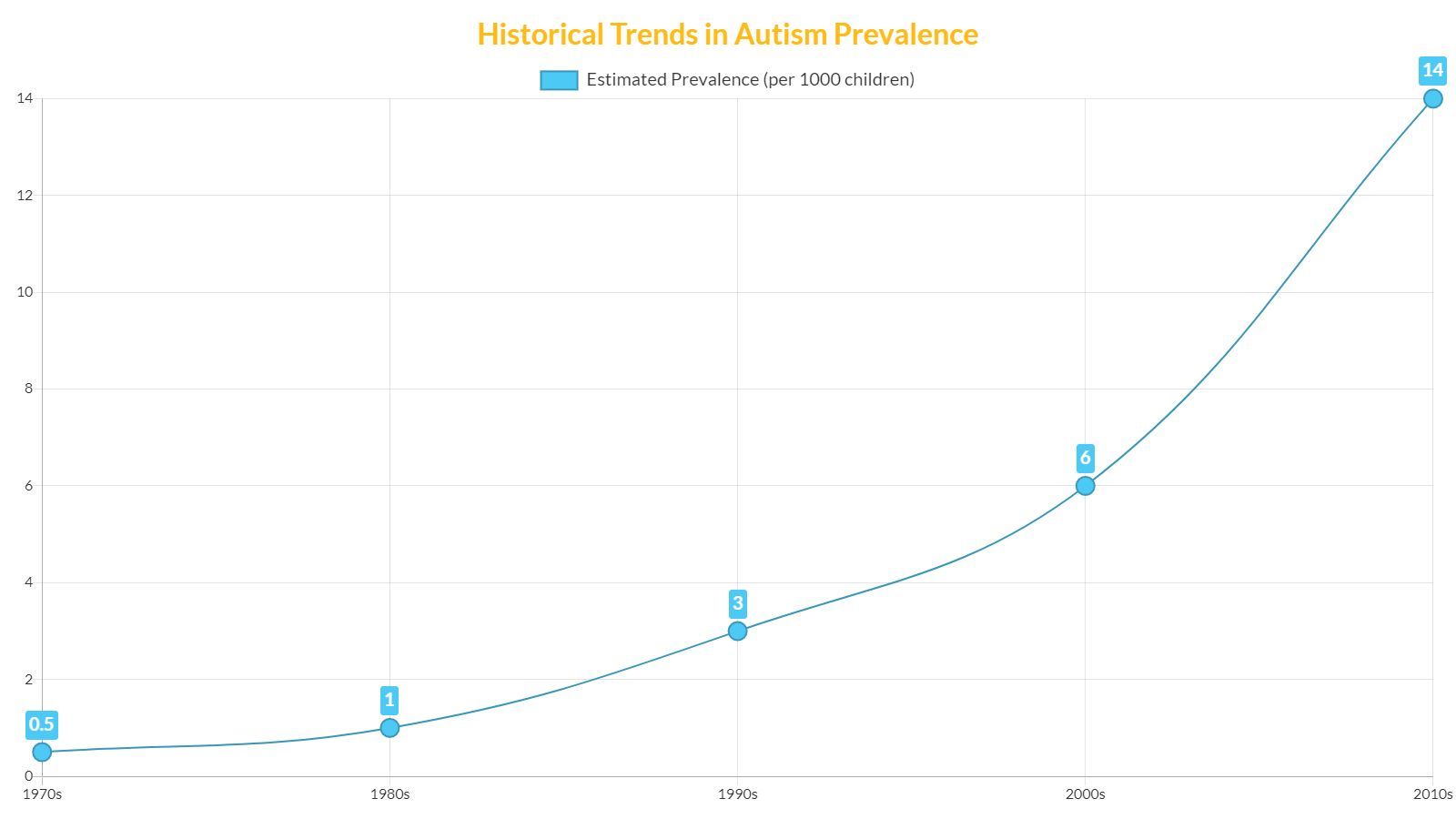
The implications of these historical trends are critical for understanding how autism is perceived and addressed in society. They also highlight the need for continued research and resource allocation.
Current Research Findings
In recent years, the focus on autism prevalence has intensified. Current research findings suggest that there are variances in autism diagnosis rates, not just across time but also among different populations and regions. For instance, the autismprevalencerates in the United States have risen, with the latest data indicating that approximately 1 in 54 children are diagnosed with ASD.
Studies also indicate a notable difference in autism prevalence by gender, showing that boys are approximately four times more likely to be diagnosed with autism than girls. This disparity raises important questions about the factors that contribute to these differences, including potential genetic, biological, and environmental influences, as well as the possibility of underdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis in girls.
The examination of current research findings also points to the importance of access to diagnostic services and the role of socioeconomic factors in the identification of autism. More comprehensive studies and improved diagnostic tools are necessary to fully understand the nuances of autism prevalence and ensure that all individuals with ASD receive the support they need.
The trends in autism prevalence have significant implications for public health policy, educational resources, and support systems. It underscores the importance of maintaining up-to-date autismspectrumdisorder statistics to guide decision-making and resource distribution to support individuals with ASD and their families.
This examination of trends, both historical and current, is vital to shaping the conversation around autism and ensuring that the needs of the autism community are met. It also highlights the dynamic nature of autism research, which continues to evolve as we gain a deeper understanding of the condition. With ongoing research, the hope is to further elucidate the factors behind these trends and improve outcomes for individuals on the autism spectrum.
Implications for Texas
The prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and the support available for individuals and families affected by ASD are critical considerations for communities. In Texas, understanding these factors is essential for providing the necessary resources and care.
Autism Rates in Texas
Recent reports indicate a significant concern regarding the prevalence of autism within the state. According to Texas Health and Human Services, the state is actively monitoring autism rates and providing information and resources to residents. The
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provide national data which can offer context for state-specific statistics.
| Age Group | Prevalence Rate in Texas |
|---|---|
| Children aged 8 years | 1 in 54 |
Data derived from CDC's most recent surveillance.
The prevalence of autism in Texas aligns with national statistics that estimate approximately 1 in 54 children are diagnosed with ASD. It's important to note that these figures represent an average and that actual rates may vary across different communities and demographics within the state. To understand the broader landscape of ASD prevalence, individuals can refer to autism prevalence rates and autism diagnosis rates.
Support and Resources
Texas offers a wide range of support services and resources for those affected by ASD. State organizations and health services provide assistance in the form of therapy, education, and community programs aimed at improving the quality of life for individuals with autism and their families.
Resources include but are not limited to:
- Early intervention programs
- Education and training for parents and caregivers
- Support groups and networks
- Access to therapeutic services such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
- Financial assistance programs
For a comprehensive list of available support and resources, families and professionals can visit the Texas Health and Human Services website on Autism in Texas. Additionally, it is beneficial for those seeking information on ASD to explore autism spectrum disorder statistics and autism prevalence worldwide to gain insight into how Texas compares to national and international trends.
Understanding the prevalence and impact of autism, particularly in Texas, is crucial for ensuring that adequate support systems are in place. As research evolves and more data becomes available, Texas continues to adapt its services to meet the needs of its residents, promoting awareness, acceptance, and inclusivity for individuals with ASD.












