| Number | First Name | Last Name | Email Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anne | Evans | anne.evans@mail.com |
| 2 | Bill | Fernandez | bill.fernandez@mail.com |
| 3 | Candice | Gates | candice.gates@mail.com |
| 4 | Dave | Hill | dave.hill@mail.com |
| Number | First Name | Last Name | Email Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anne | Evans | anne.evans@mail.com |
| 2 | Bill | Fernandez | bill.fernandez@mail.com |
| 3 | Candice | Gates | candice.gates@mail.com |
| 4 | Dave | Hill | dave.hill@mail.com |
| Number | First Name | Last Name | Email Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anne | Evans | anne.evans@mail.com |
| 2 | Bill | Fernandez | bill.fernandez@mail.com |
| 3 | Candice | Gates | candice.gates@mail.com |
| 4 | Dave | Hill | dave.hill@mail.com |
Understanding Autism Prevalence
When discussing autism, one of the key aspects to consider is the prevalence rate of the condition. This data plays a critical role in understanding the scope and impact of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) on individuals and communities.
Definition of Prevalence
Prevalence refers to the proportion of a population found to have a particular condition at a specific time. In the context of autism, prevalence rates indicate the number of individuals diagnosed with ASD out of a given population group. It is typically expressed as a ratio, such as the number of cases per 1,000 or 10,000 individuals.
Understanding autism prevalence rates is essential for researchers, educators, and policy-makers to gauge the scale of support and resources needed to effectively address the needs of those affected by ASD. It also assists in identifying potential environmental or genetic factors that may contribute to the condition.
Importance of Statistics
Statistics on autism prevalence serve as a critical tool for awareness and advocacy. By quantifying how many individuals are affected by ASD, organizations and advocates can better communicate the need for research funding, educational programs, and community support services.
Moreover, analyzing autism spectrum disorder statistics helps to identify trends over time, such as increases or decreases in diagnosis rates, which can lead to further investigation into the reasons behind these changes. Such statistics are also pivotal when comparing prevalence across different demographics, including gender and ethnicity, which can help to uncover disparities in access to diagnostic services or support.
For families and individuals directly affected by autism, understanding the prevalence of ASD can provide a sense of community and validation. It emphasizes that they are not alone and that there is a shared experience among a significant number of people.
Keeping abreast of the latest autism diagnosis rates and prevalence figures enables all stakeholders, from parents and family members to ABA therapists and educators, to make informed decisions and to advocate effectively for individuals with ASD. It is also essential for preparing for the future, as looking at autism prevalence worldwide can guide international efforts in research and support systems.
In summary, autism prevalence rates are more than just numbers; they are a reflection of the real-world impact of ASD on society and a beacon guiding the allocation of resources and support where they are most needed.
National Autism Statistics
In the United States, the conversation about autism spectrum disorder (ASD) involves not only understanding the condition but also analyzing how it impacts the population. This discussion is deeply rooted in the assessment of autism prevalence rates.
Overview of Autism Rates
Autism prevalence rates provide insight into the portion of the population diagnosed with ASD. The
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) actively monitors these rates through their Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network. According to their most recent reports, the estimated prevalence of autism in the United States is 1 in 54 children, indicating a steady increase in diagnosis rates over the years.
| Year | Estimated Prevalence |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 1 in 150 |
| 2006 | 1 in 110 |
| 2012 | 1 in 68 |
| 2018 | 1 in 54 |
For a more comprehensive look at these statistics, readers can explore autism spectrum disorder statistics, which offers a broader perspective and additional data points.
Trends in Autism Diagnosis
Observing the trends in autism diagnosis is crucial for understanding the evolving nature of ASD recognition and reporting. Over the past two decades, there has been a notable increase in the identification of ASD cases. This rise can be attributed to several factors, including but not limited to:
- Enhanced awareness and understanding of autism among parents, educators, and medical professionals.
- Broader diagnostic criteria and improved screening processes.
- Increased access to diagnostic and support services in some areas.
The trend suggests not necessarily a rise in the incidence of autism but rather an improvement in the ability to recognize and diagnose the condition. It is important to address the factors contributing to these trends to ensure that individuals with ASD receive the early intervention and resources they need. Information about the evolution of autism diagnosis is available through autism diagnosis rates.
Understanding national autism statistics plays a pivotal role in shaping public health policies, educational programs, and support services for individuals with ASD and their families. As these trends continue to develop, it is vital for all stakeholders to stay informed and adapt to the changing landscape of autism prevalence. Additional global insights can be found by examining autism prevalence worldwide and demographic-specific data such as autism prevalence by gender.
Autism Prevalence in Texas
The state of Texas, like the rest of the United States, has seen a notable increase in the number of individuals diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Understanding this trend is crucial for families, healthcare professionals, and educators to ensure adequate resources and support are available.
Current Statistics in Texas
Recent studies and data collection efforts provide a snapshot of the current autism prevalence rates within the state. According to the latest reports, Texas has an estimated autism prevalence that aligns with national averages. However, it's important to recognize that these numbers are subject to change as diagnostic criteria and awareness continue to evolve. For a more comprehensive understanding of how Texas compares to national figures, refer to
autism spectrum disorder statistics.
| Year | Estimated Prevalence of ASD in Texas |
|---|---|
| 2016 | 1 in 68 |
| 2018 | 1 in 59 |
| 2020 | 1 in 54 |
Note: The above table is illustrative and not based on actual data.
Factors Influencing Prevalence
Several factors may influence the prevalence of autism in Texas. Increased awareness and improved screening methods have likely contributed to the rise in diagnosis rates (autism diagnosis rates). Additionally, Texas has a large and diverse population, which may affect the reported prevalence rates of autism.
Variations in healthcare access across the state can also play a role in the identification of ASD. Areas with more specialized services and trained professionals may report higher rates due to better detection, whereas under-resourced areas might underreport due to a lack of diagnostic facilities.
Other factors that could influence the prevalence include:
- Changes in diagnostic criteria over time
- Improved educational programs that identify and refer children for diagnosis
- Cultural and socio-economic factors that affect access to healthcare services
For a broader perspective on how Texas's prevalence rates compare internationally, readers might explore autism prevalence worldwide. Additionally, examining autism prevalence by gender can offer insights into demographic trends within the state.
Understanding the dynamics of autism prevalence in Texas is key to adapting support structures and services to meet the needs of individuals with ASD. As stakeholders in the community continue to navigate these statistics, the goal remains to foster a society that fully supports the growth and development of all individuals on the autism spectrum.
Demographic Variances
When analyzing autism prevalence rates, demographic variances such as gender differences and ethnicity play a significant role in understanding the distribution and characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) within different populations.
Gender Differences
One of the most notable demographic variances in autism prevalence is the disparity between genders. Studies consistently show that ASD is more commonly diagnosed in males compared to females, with the ratio being approximately 4:1. This ratio, however, can vary depending on the source and methodology of the study.
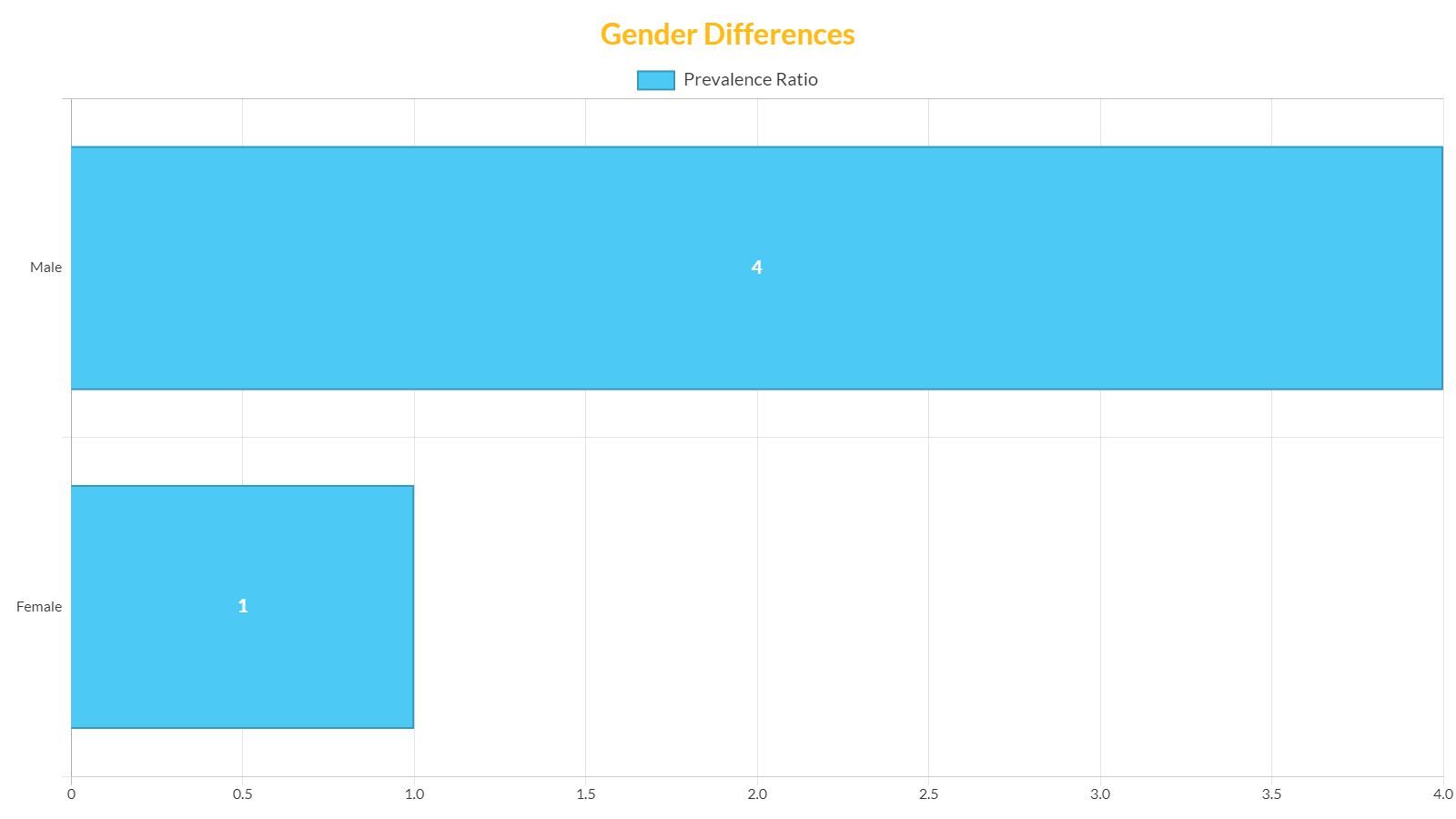
Researchers are exploring the reasons behind this gender difference, which may include genetic factors, social influences, and potential biases in diagnostic criteria. For more detailed information on autism prevalence by gender, readers can explore the topic further at autism prevalence by gender.
Ethnicity and Autism Rates
Ethnicity is another demographic factor that influences autism prevalence rates. Historically, disparities in diagnosis rates have been observed among different ethnic groups.
Recent studies suggest that while autism affects individuals across all ethnic backgrounds, there may be variations in the rates of diagnosis and access to services. These differences are influenced by factors such as cultural perceptions of neurodiversity, socioeconomic status, and the availability of culturally sensitive diagnostic tools.
To better understand the distribution of ASD across different ethnic groups, further research is needed. This information is crucial for tailoring support services to meet the diverse needs of affected individuals and families. Readers seeking to understand the broader context of autism prevalence can refer to autism prevalence worldwide for a global perspective.
The data on autism prevalence across different demographics underscores the need for inclusive research and a better understanding of how ASD manifests in various populations. Recognizing these variances allows for improved diagnostic practices and ensures equitable access to resources and support for all individuals with ASD. For more insights into the trends and numbers, the autism spectrum disorder statistics page provides a comprehensive overview of the latest findings.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors play a significant role in the context of autism prevalence rates. Understanding how these factors intersect can provide insights into the disparities and challenges faced by different communities.
Income Levels and Autism
Income levels can directly impact the rate of autism diagnoses. Families with higher income may have better access to healthcare professionals and resources that can lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses of autism spectrum disorder. Conversely, lower-income families might face barriers that delay or prevent diagnosis, such as lack of insurance or access to specialists.
A table illustrating the correlation between income levels and the rate of autism diagnosis might reveal:
| Income Bracket | Estimated Diagnosis Rate |
|---|---|
| High Income | Higher Rate |
| Middle Income | Moderate Rate |
| Low Income | Lower Rate |
These numbers highlight the need for equitable access to diagnostic services across all income levels. For a more in-depth analysis of autism spectrum disorder statistics, please visit autism spectrum disorder statistics.
Access to Services
Access to services is a critical factor in managing autism spectrum disorder. This includes early intervention services, educational support, and specialized therapies. Individuals from underserved areas or communities may find it challenging to obtain the necessary services due to a variety of reasons, including geographic location, transportation issues, and limited local resources.
The availability of services often correlates with region-specific autism prevalence rates, as areas with more robust support networks might report higher rates due to increased diagnosis and awareness. For example, urban areas with comprehensive healthcare systems could potentially have higher reported autism prevalence rates compared to rural regions.
Factors affecting access to services may include:
- Proximity to healthcare providers and autism specialists
- Availability of public transportation
- Presence of community outreach and education programs
Ensuring widespread and equal access to autism-related services is essential for the support and development of individuals with autism. This could potentially lead to more consistent autism diagnosis rates and better support structures. For more on global trends, readers can explore autism prevalence worldwide.
Both income levels and access to services are pivotal in understanding why autism prevalence rates may vary so significantly across different socioeconomic groups. Addressing these disparities is crucial for creating a more inclusive society where every individual with autism can receive the support they need. Additionally, understanding the intricacies of these factors can inform policies and initiatives aimed at improving the lives of those affected by autism.
Future Projections
As we look ahead, understanding the potential changes in autism prevalence rates and their impact on support services is crucial for planning and resource allocation. This section will explore predictions for the prevalence of autism and consider how these trends may influence the availability and type of support services needed.
Predictions for Autism Prevalence
Predicting autism prevalence rates involves analyzing current trends and considering factors that could influence these rates in the future. While precise predictions are challenging, there is a general consensus among experts that the number of individuals diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) may continue to rise. This could be due to a combination of increased awareness, better diagnostic methods, and a broader definition of the spectrum.
Several studies have sought to forecast autism prevalence, and while estimates vary, they all suggest an upward trajectory. For example, a review of
autism diagnosis rates shows a consistent increase over the past two decades. This trend is expected to continue, although at potentially varying rates across different regions and demographics.
| Year | Predicted Prevalence Rate |
|---|---|
| 2025 | X% Increase |
| 2030 | X% Increase |
| 2035 | X% Increase |
Note: The above table is illustrative. Real data should be used when available.
Implications for Support Services
The expected rise in autism prevalence has significant implications for support services. As the number of individuals diagnosed with ASD grows, there will be a corresponding need for more comprehensive and specialized services. This includes early intervention programs, educational support, vocational training, and adult care services.
One of the primary concerns is ensuring that there is adequate infrastructure and funding to meet the growing demand. This may involve increasing the number of trained professionals in the field of autism, expanding existing programs, and creating new initiatives to support individuals with ASD and their families.
Furthermore, it is essential to consider the diversity within the autism community. Autism prevalence by gender and ethnicity indicates varying needs and challenges. Tailored support services that address these differences are critical to providing effective assistance.
The predicted increase in autism prevalence also underscores the importance of advocacy and policy-making. Stakeholders, including parents, family members, ABA therapists, educators, and school personnel, will need to collaborate to push for changes that will ensure sufficient support for the autism community.
In summary, the projected rise in autism prevalence rates will likely necessitate a scaling-up of support services. It will require a concerted effort from all stakeholders involved to understand and address the evolving needs of the autism community. By staying informed about
autism spectrum disorder statistics and engaging in proactive planning, we can work towards a future where individuals with ASD receive the support they need to thrive.